We guarantee 100% confidentiality
WHAT WE DO?
Control Search Results
Take charge of your online reputation. Using cutting-edge software, our in-house SEO experts, professional writers, legal tools, and advanced algorithm knowledge, we can craft a plan to promote the content you want visible while pushing negative content off the first page.
-
The average Google Search session is just under 1 minute. This means that within 1 minute the average user has already made
-
Up to 72% of people will make a decision to avoid you upon finding negative content online; and
-
88% of consumers trust online content as much as a personal recommendation.
Google Orgranic CTR Breakdown by Position
If bad press ranks in the first few positions of Google for your brand or name, it's a major problem because most users never scroll past the first few results—and click-through rate (CTR) becomes a key signal that can either help bury the bad press or make it stick longer.
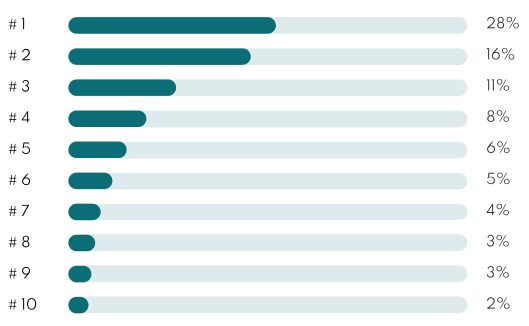
| Option | Effectiveness | Cost |
| #1. Wait For Articles To Fall Off | Low | Free |
| #2. Submit a DMCA Complain | Low | Free |
| #3. Hire a Reputation Expert - Ross Kernez | High | $$ |
| #4. Reach Out To Journalists | Low | Free |
| #5. File a Defamation Lawsuit | Medium | $$$ |
| #6. Request an Update To Article | Low | Free |
| #7. Create Social Media Profiles | Medium | Free |
| #8. Create New Websites | Medium | $$ |
| #9. Become a Writing Contributor | Medium | $ |
| #10. Create Backlinks & Digital PR | Medium | $$ |
Relying on the freshness algorithm, also known as the Freshness Systems, to let negative articles naturally fall off the first page of search results is often not a viable strategy for managing your online reputation, especially if you want to take down negative results from Google quickly. Search engines like Google prioritize newer content, and if negative content continues to generate clicks, shares, or backlinks, it may maintain its ranking regardless of its age. Therefore, depending solely on the freshness algorithm is risky and can leave your reputation vulnerable for an extended period.
Hiring an experienced reputation expert specializing in online reputation management can expedite this process by actively working to displace negative content with positive, relevant information. An expert can ensure that any new negative content is swiftly addressed and managed. They can implement strategies to prevent negative articles from gaining traction, such as monitoring your online presence, responding to negative feedback appropriately, and continually updating and optimizing positive content.
To submit a DMCA (Digital Millennium Copyright Act) takedown notice to Google, you must follow a formal process. Begin by identifying the infringing content and locating the URLs of the specific pages containing the infringing material. Gather evidence that proves the content infringes on your copyright.
Next, submit the notice to Google by visiting Google’s DMCA page at https://support.google.com/legal/troubleshooter/1114905. Select the appropriate product (e.g., Search, YouTube) and follow the prompts to fill out and submit the form.
After submitting, monitor the process, as Google will review the notice and may contact you for additional information. If the notice is found valid, Google will take down the infringing content from their search results.

An experienced SEO expert like Ross Kernez employs advanced suppression techniques that he developed over years to influence search engine results, utilizing positive news content, creating new websites, publishing favorable press and leveraging social media presence to suppress negative results on Google. He will develop a custom strategy tailored to your specific needs, ensuring that positive stories about you or your business are prominently displayed in search results. By improving the visibility of favorable content, he can effectively suppress negative search results.
Reaching out to a journalist to request removal or revision of a damaging article is one of the most effective—but sensitive—ways to remove bad press from Google and get rid of bad press before it spreads further. Begin by pinpointing the exact reporter and publication behind the negative story, then study their stated policies for corrections or updates. Your email should pair professionalism with empathy: acknowledge the journalist’s duty to report accurately, but demonstrate—factually and calmly—how the current piece harms your reputation or misleads readers.
In your outreach, lead with a concise explanation of why the article no longer reflects the truth or presents incomplete context. Support that claim with clear evidence: court documents, updated data, expert statements, or proof the information is outdated. Offer an easy path forward—whether that’s a formal correction, a clarifying update, or a full retraction—so the journalist sees a solution, not just a complaint. By respecting journalistic integrity while presenting compelling proof, you dramatically improve the odds of having harmful content amended or removed, helping you push down negative search results and maintain a positive online presence.
Exploring legal avenues—such as filing a defamation lawsuit to remove bad press from Google—may seem like a logical solution, but it often creates more problems than it solves. While the intent behind legal action is to protect your reputation, lawsuits can trigger unintended consequences that make it harder to get rid of bad press effectively. In many cases, legal efforts only draw more attention to the very content you're trying to suppress.
One major reason this approach is risky is the complexity and high cost of litigation. Defamation lawsuits can be lengthy, emotionally draining, and financially burdensome, with no guaranteed success. Legal fees alone can run into the tens or hundreds of thousands of dollars, and court cases can drag on f
A smart, low‑conflict tactic to remove bad press from Google and get rid of bad press is to ask the original journalist for an update or clarification. Because this process is sensitive, approach it with respect and a spirit of collaboration rather than confrontation. By framing your outreach around accuracy and transparency, you show the reporter that your goal is a balanced, fact‑based story—not censorship. This mindset alone can soften resistance and improve the odds that the article will be revised, thereby reducing its negative impact on your search results.
Maintain a courteous, professional tone that acknowledges the journalist’s role and expertise. Express appreciation for their work before outlining specific concerns, and avoid accusatory language that might trigger a defensive response. Emphasize that you value truthful reporting and want readers to have the most up‑to‑date information. When the request feels like a joint effort to enhance accuracy, journalists are more inclined to listen—and Google rewards updated, authoritative content, which in turn helps bury older negative narratives.
Support your request with clear, verifiable evidence: official documents, updated statistics, or new achievements that correct or balance the original coverage. Provide links to primary sources or attach relevant files so the reporter can fact‑check quickly. Concrete proof distinguishes your appeal from mere reputation repair and signals genuine commitment to honesty. When journalists have irrefutable data at their fingertips, updating the story becomes a straightforward editorial decision rather than a risky concession.
One of the fastest ways to remove bad press from Google and get rid of bad press is to create authoritative social media profiles that you fully control. When you claim your name or brand handle on platforms like LinkedIn, X (formerly Twitter), Instagram, and TikTok, you occupy high‑authority domains that routinely rank on page one of Google. Each profile becomes a branded asset that pushes negative links farther down the search results, limiting their visibility and influence.
Beyond visibility, social channels let you shape the narrative in real time. Regularly posting valuable content—industry insights, success stories, and authentic behind‑the‑scenes moments—signals to search engines and human audiences alike that your brand is active, transparent, and trustworthy. Responding promptly to comments or reviews also demonstrates accountability, helping neutralize lingering doubts created by earlier bad press.
To ensure these profiles outrank legacy negativity, apply proven SEO techniques: use a consistent brand name in the @handle and display name; fill out every bio field with keyword‑rich descriptions; include a backlink to your primary website; and publish multimedia content that earns shares and backlinks. When optimized correctly, social accounts create a protective wall of fresh, authoritative results, dramatically improving your chances of burying negative coverage and reclaiming your online reputation.
Launching fresh, well‑optimized websites is a powerful tactic to remove bad press from Google and get rid of bad press. Unlike social platforms—where algorithms and policies can shift overnight—your own sites give you full control over every headline, image, and meta tag that shapes your online narrative. Each domain you own occupies valuable real estate on page one of search results, crowding out negative or outdated coverage that no longer reflects who you are today.
A dedicated website lets you showcase expertise, success stories, and thought‑leadership content under your direct editorial oversight. When built with solid technical SEO—clean code, fast load times, secure HTTPS, and schema markup—your new site can outrank legacy negativity by signaling higher relevance and authority to Google. Strategic internal linking, keyword‑rich blog posts, and backlinks from credible sources further boost visibility, making it harder for bad press to regain top positions.
Treat each site as a reliable hub for audiences, journalists, and potential partners to verify accurate information about your brand. Include an “About” page that clarifies your mission, a media center with press‑ready assets, and timely case studies that demonstrate ongoing impact. Over time, this ecosystem of branded websites creates a strong defensive barrier, ensuring that positive, up‑to‑date content dominates search results and pushes harmful links out of sight.
Few tactics boost credibility faster than publishing articles in respected industry outlets. By becoming a regular contributor, you not only remove bad press from Google and get rid of bad press but also flood search results with authoritative, positive narratives. Search engines reward content on reputable domains, so every byline you earn can outrank legacy negativity, pushing it down the page and out of public view.
Thought‑leadership pieces showcase your unique insights, positioning you as the go‑to expert in your field. Over time, this consistent stream of high‑quality content builds trust with prospective clients, investors, and journalists—an invaluable defense against future reputation threats. Guest contributions also expand your professional network, opening doors to speaking engagements, partnerships, and backlinks that further strengthen your online presence.
To maximize impact, target publications whose audiences align with your goals and ensure each article links back to your branded websites or optimized social profiles. This strategic interlinking signals relevance and authority to Google, accelerating the suppression of negative results and cementing your reputation as a credible, proactive thought leader.
Strategic backlink building and digital PR campaigns form a powerful one‑two punch to remove bad press from Google and get rid of bad press. When high‑authority sites link to your content, they pass on “trust signals” that Google’s algorithm uses to rank pages. Each quality backlink raises the perceived value of your positive assets—blog posts, case studies, media kits—allowing them to outrank negative or outdated coverage and push it off the first page.
Digital PR takes that momentum further by placing your story in online news outlets, influential blogs, and niche industry publications. These earned media features not only introduce you to new audiences but also generate natural backlinks from reputable domains. The result is a virtuous cycle: your visibility rises, journalists see you as a credible source, and fresh PR opportunities appear—each reinforcing the others and steadily burying harmful search results.
To maximize suppression impact, focus on relevance and authority: pitch publications whose readership aligns with your brand, craft data‑driven narratives that editors love, and secure do‑follow links to your most important pages. Combined with ongoing backlink analysis and outreach, this approach delivers a durable reputation shield—ensuring that positive, high‑value content dominates search results and harmful links fade into obscurity.
What exactly counts as “bad press,” and how can I tell if something online qualifies?
Bad press includes any online article, blog post, social‑media thread, or forum comment that paints an inaccurate, outdated, or unfair picture of you or your brand. Even neutral coverage can become “bad” if the headline is sensational, the facts are wrong, or the context is missing. Searchers rarely dig past the first page of Google, so a single negative snippet can disproportionately influence perception. If a piece drives inquiries that question your credibility, prompts customers to hesitate, or triggers uncomfortable conversations with partners, it’s bad press. You can measure its impact by tracking dips in traffic, sales, or inbound leads that correlate with the article’s publication or rise in ranking.
Why is it so hard to delete negative press coverages from Google once it shows up?
Google’s algorithm rewards content that is popular, well‑linked, and frequently clicked—attributes that sensational negative stories often possess. Major news sites carry high domain authority, making it tough for newer positive pages to outrank them organically. Legal takedowns are limited to clear defamation, copyright violations, or privacy infringements, and they take time. Even if you succeed with a takedown, cached copies or syndicated versions can reappear. As a result, a comprehensive reputation strategy usually focuses on burying bad press rather than relying solely on removal.
Can I request Google directly to delete negative press coverages ?
Google rarely removes lawful content just because it’s unflattering. To qualify for de‑indexing, you generally must prove the content violates specific policies—for example, containing sensitive personal data, explicit harassment, or illegal material. Even then, Google may only apply a regional or partial block. Most reputational issues fall outside these narrow categories, forcing individuals and businesses to pursue other avenues such as outreach to the publisher, negotiation, or strategic suppression. Therefore, “How to Remove Bad Press from Google & Get Rid of Bad Press” typically means leveraging SEO, PR, and content strategy rather than direct deletion.
How long does it usually take to push down bad press coverage on the first page of Google results?
Timelines vary based on the authority of the negative source, the competitiveness of your name or brand, and the resources you commit. For local news on a low‑authority site, impactful movement can occur in a few weeks; for nationally syndicated stories on high‑authority domains, expect several months. Consistent publication of optimized content, backlink acquisition, and targeted digital PR all shorten the timeline by signaling relevance and authority to Google’s algorithm. Progress is often nonlinear—you might see a negative result drop five spots overnight, then bounce back before settling lower long‑term. An experienced reputation manager will map milestones so you understand what “steady progress” looks like in your situation.
Is paying for Google Ads a quick fix for bad press on organic search?
Running branded search ads can temporarily place your chosen message above organic listings, giving you immediate control of the first thing users see. However, ads are clearly labeled and disappear when budget or campaigns end, while negative organic links remain. Ads don’t influence the underlying algorithm, so they don’t actually remove or get rid of bad press. Still, ads can buy breathing room while long‑term suppression tactics take effect. They also let you A/B‑test messaging that can inform your organic content strategy.
What tactics do online reputation experts use to delete negative press coverages ?
Experts begin with a forensic audit to catalog every mention—positive, neutral, and negative—then prioritize targets based on visibility and impact. Next, they create or improve authoritative assets you control, such as your website, social profiles, and thought‑leadership articles, optimizing each for your key terms. They secure third‑party coverage in reputable outlets to add credibility and backlinks. Structured data, internal linking, and media diversification—videos, podcasts, slide decks—all signal to Google that your brand owns fresh, multifaceted authority. The final layer is ongoing monitoring to catch emerging negativity early before it gains traction.
Are press‑release distribution services worth using to combat bad press?
Press releases can seed positive narratives quickly and may earn pickups on high‑authority domains, but modern SEO values originality and depth over mass‑syndication. A press release should be part of a broader content plan that includes unique opinion pieces, interviews, and multimedia assets. If the release simply repeats marketing copy, it rarely ranks high enough to displace a negative story. When crafted with newsworthy angles, timely data, and genuine insights, a press release can attract journalists, backlinks, and social shares that collectively push negative results down. Think of distribution as an amplifier, not a silver bullet.
Does deleting my social‑media accounts help remove bad press?
Shutting down platforms may feel cathartic, but it often does the opposite of burying negativity. Active, optimized social profiles occupy valuable real estate on page one for branded searches, which crowds out harmful links. Deleting accounts leaves a vacuum that negative stories can fill more easily. Instead, revitalize your profiles with consistent, high‑value content—share press hits, industry commentary, and behind‑the‑scenes updates that reinforce credibility. Social engagement also creates fresh signals that Google favors, accelerating suppression efforts.
Can positive customer reviews help push down negative news articles?
Yes—reviews on high‑authority platforms like Google Business Profile, Trustpilot, or industry‑specific sites frequently rank for brand‑name searches. A steady stream of authentic, detailed reviews adds trust signals for both algorithms and human searchers. Encourage satisfied customers to mention specifics (products, services, and location) because richer text helps those review pages rank higher. Coupled with schema markup on your website, reviews can surface as star‑ratings in search snippets, which draw clicks away from negative coverage. Over time, this engagement data contributes to ranking shifts in your favor.
What legal remedies exist if a negative article is defamatory?
If statements are demonstrably false and damage your reputation, you can issue a retraction request or pursue litigation for defamation. A formal legal notice often prompts publishers to correct or remove the story, especially if you provide clear evidence. Courts can issue injunctions requiring takedown or awarding damages, but litigation is costly, public, and slow. Reputation specialists often consult defamation attorneys to determine whether legal action makes strategic sense. Even when successful, legal victories should be paired with SEO work to ensure removed content doesn’t linger in search caches.
How much does professional reputation management cost?
Pricing depends on scope: the number of negative assets, authority of the domains hosting them, and complexity of your brand environment. Basic suppression campaigns for a single harmful link might start around $2,000 per month, while multi‑layer efforts for public figures can exceed $10,000 monthly. Good agencies outline deliverables—content pieces, backlinks, media placements—and provide transparent progress reports. Cheaper “quick‑fix” providers who guarantee instant removal often rely on risky techniques that can backfire. View the expense as an investment in brand equity, akin to advertising or legal protection.
Is it possible to do reputation repair on my own without hiring experts?
DIY approaches—blogging, updating social profiles, requesting edits from publishers—can move the needle for low‑competition personal names or niche brands. You’ll need a solid grasp of SEO, PR outreach, and content strategy to achieve measurable suppression of entrenched bad press. Time commitment is substantial; think hours every week for months. Mistakes such as spammy link‑building or thin content can trigger Google penalties, worsening visibility. Many clients begin DIY, then hire experts when progress stalls or new negative results appear.
How do you measure success in a reputation‑recovery campaign?
Key indicators include the downward movement of negative URLs, upward movement of positive or neutral assets, and overall sentiment of page‑one search results. Analytics should track organic click‑through rates, branded‑search volume, and conversions influenced by brand‑name queries. Qualitative feedback—from prospects, partners, or journalists—often reveals improved perception before rankings fully stabilize. A reputable agency provides dashboards that map keyword positions and media placements relative to baseline data. Because algorithms constantly evolve, success entails not just hitting a ranking milestone but maintaining it.
Will creating a new business entity hide past negative articles about me?
Re‑branding or forming a new entity can confuse search algorithms temporarily, but journalists and savvy customers quickly uncover ownership ties. Legacy coverage often references former brand names and personal identifiers, which remain searchable. Google’s knowledge graph links related entities, so negativity can follow you across rebrands. A better approach is to proactively publish the new brand story—addressing lessons learned, demonstrating changes, and giving journalists positive angles to update their coverage. Embracing transparency signals authenticity and limits future negative narratives.
How often should I publish new content to keep bad press buried?
Consistency matters more than sheer volume. For most brands, weekly blog posts, bi‑weekly thought‑leadership articles, and daily social‑media updates create enough freshness signals. Evergreen pieces—case studies, white papers, and video explainers—anchor long‑term authority, while timely posts around industry news offer spikes in relevance. Diversify formats to appeal to different search intents and SERP features (news carousels, video packs, FAQs). A cadence audit every quarter ensures you’re not merely producing content but strategically filling gaps in the search landscape.
Does negative SEO from competitors make bad press rank higher?
In rare instances, malicious actors can build spam links to amplify a damaging article or create duplicate content that boosts its perceived relevance. Google’s algorithms generally ignore or neutralize low‑quality links, but coordinated attacks can skew short‑term visibility. Monitoring backlink profiles with tools like Ahrefs or Google Search Console alerts you to suspicious spikes. A disavow file and a surge of high‑quality backlinks to positive assets usually restore balance. Documenting evidence helps if you later pursue legal remedies for unfair competition.
Are paid influencer shout‑outs useful for pushing negative stories down?
Influencer content can generate immediate buzz, social engagement, and backlinks, all of which help dilute bad press. However, sponsored posts alone seldom rank in Google unless hosted on the influencer’s blog or repurposed into longer‑form media. For lasting impact, integrate influencer collaborations into a broader campaign—guest articles, joint webinars, or co‑created whitepapers—so the content lives on multiple high‑authority domains. Always tag sponsored posts properly to comply with platform rules; transparency builds trust and avoids penalties that could negate your efforts.
What happens if I ignore bad press and hope it fades away?
Silence often signals guilt or indifference to observers, which can worsen reputational damage. Negative stories may gather backlinks and social shares over time, solidifying their search positions. Competitors might leverage them in sales pitches, and journalists may resurface the content during future coverage. Meanwhile, potential customers, partners, and investors form opinions without hearing your side. Proactive engagement—correcting inaccuracies, publishing counter‑content, and highlighting positive developments—prevents a one‑sided narrative from defining your brand.
Will AI tools help automate the process of deleting negative press coverages from Google?
AI can accelerate tasks such as sentiment analysis, keyword clustering, and content ideation, freeing experts to focus on strategy and outreach. Machine‑learning models flag emerging negative chatter early, enabling faster response. However, AI alone cannot negotiate with editors, secure top‑tier media coverage, or build genuine relationships for backlink acquisition. Human oversight remains essential to ensure nuanced storytelling, legal compliance, and ethical standards. View AI as a force multiplier—not a replacement—for experienced reputation professionals.
How do I maintain a clean online reputation once the bad press is gone?
Think of reputation as a living asset that needs regular maintenance, similar to cybersecurity or brand design. Schedule quarterly audits of search results and social sentiment to catch new issues quickly. Encourage continuous positive coverage through expert commentary, community involvement, and customer success stories. Maintain robust media relationships so journalists approach you for clarifications rather than relying on outdated sources. Finally, codify crisis‑response protocols so your team reacts swiftly if fresh negativity emerges, ensuring “How to Remove Bad Press from Google & Get Rid of Bad Press” becomes preventative rather than reactive.